The archaeological site at Sinauli in Uttar Pradesh has provided significant insight into ancient burial practices, gender identities, and social hierarchy in South Asia. The evidence uncovered at Sinauli challenges long-held assumptions and offers fresh perspectives on mortality, gender roles, and elite status in ancient Indian society.
Location and Historical Context
Sinauli is situated in the Baghpat district of western Uttar Pradesh, lying within the fertile Upper Ganga-Yamuna Doab region. It is associated with the Ochre Coloured Pottery (OCP) culture, which dates back to the early second millennium BCE. This site gained attention due to its unique burial practices, especially those involving women and the material assemblages found with their graves.
Overview of Excavations
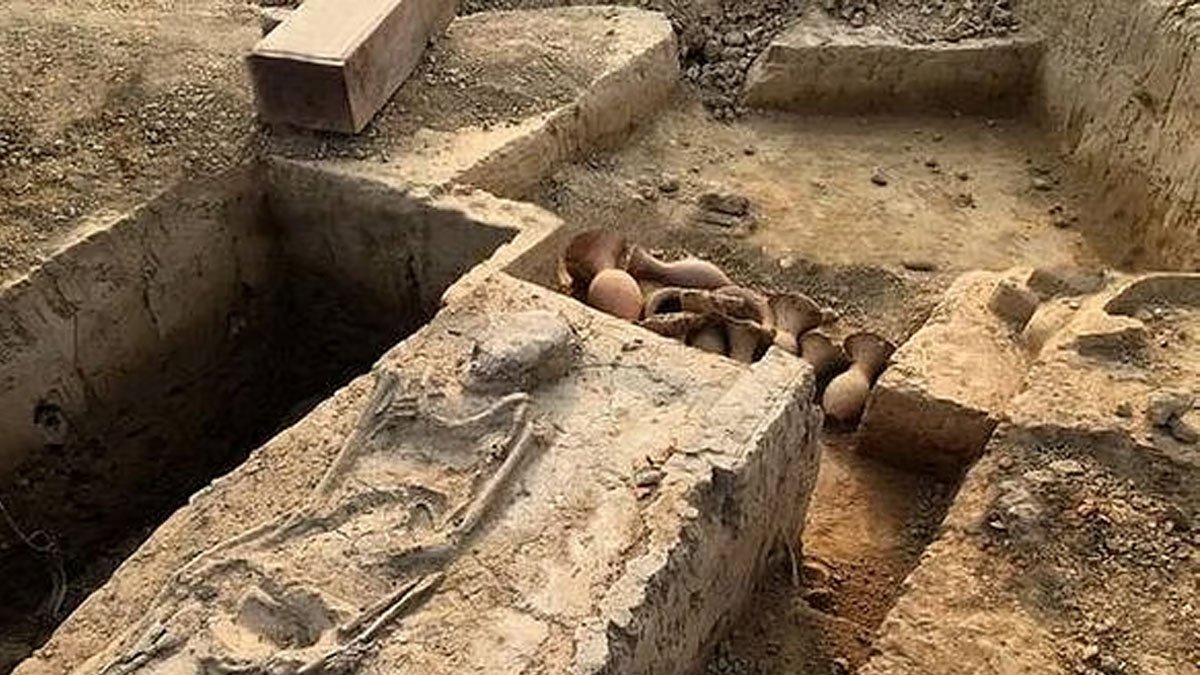
The Sinauli excavations were initiated in 2005 under archaeologist D.V. Sharma, and further work was conducted in 2018 by Dr. Sanjay Manjul. In 2005, archaeologists uncovered 116 burials, typically oriented north-south, along with ochre-colored pottery. The 2018 excavations revealed even greater complexity, including wooden coffins adorned with copper sheets, rectangular boxes, antenna swords, helmets, shields, pots, and controversial wheeled vehicles—leading to a debate over whether these were chariots or carts.
Types of Burials
Sinauli yielded four primary burial types:
– Symbolic burials without skeletons.
– Primary burials with full skeletons.
– Secondary or fragmented burials.
– Multiple burials containing fragmented remains.
Gender Distinctions in Burial Practices
A significant contribution of Sinauli is its challenge to conventional views on gender and mortuary archaeology. Certain burials, notably those identified by Asko Parpola, show that elite women were sometimes interred in richly decorated coffins with martial symbols such as swords, shields, and wheeled vehicles. Coffins for women featured steatite inlay and were often covered, in contrast to men’s coffins, which generally had copper sheathing and were left uncovered. Such differentiation suggests elaborate symbolism surrounding gender and possibly ritual seclusion or heightened sacredness for women in death.
One highly debated aspect is the absence of feet in Burial-1, which might suggest less earthly mobility or represent a transformation from earthly to transcendent status.
Rethinking Weaponry and Gender
The presence of weapons, such as copper antenna swords and shields, in women’s graves at Sinauli has prompted scholars to reconsider rigid notions of gender roles. These martial objects could signal the dead’s authority—either as warriors or ritual leaders—thus broadening our understanding of gender within ancient funerary contexts. Interestingly, such elaborate martial symbolism is less prevalent in the male burials at Sinauli.
Symbolism of Coffins and Elite Status
Coffins at Sinauli, rare in South Asian archaeology, were more than mere containers; they symbolically transformed the deceased into sacred beings. Their intricate decoration reflects considerable labor, resources, and craftsmanship, indicating elite status and the possibility of gendered authority within the social hierarchy.
Conclusions and Implications
The burial evidence from Sinauli emphasizes material distinctions that reveal social stratification, hierarchy, and constructed gender roles. While the idea of women warriors remains debated, the presence of martial symbols with elite women points towards complex rituals and conceptions of social power in death. Sinauli thus stands out as a crucial site for rethinking gender identities, social class, and the symbolic aspects of funerary practices in ancient India.

 Events2 years ago
Events2 years ago
 Videos3 years ago
Videos3 years ago
 Events11 months ago
Events11 months ago
 Videos11 years ago
Videos11 years ago
 Events10 months ago
Events10 months ago