articles
FAMINES during British Rule
Published
5 years agoon
By
ihar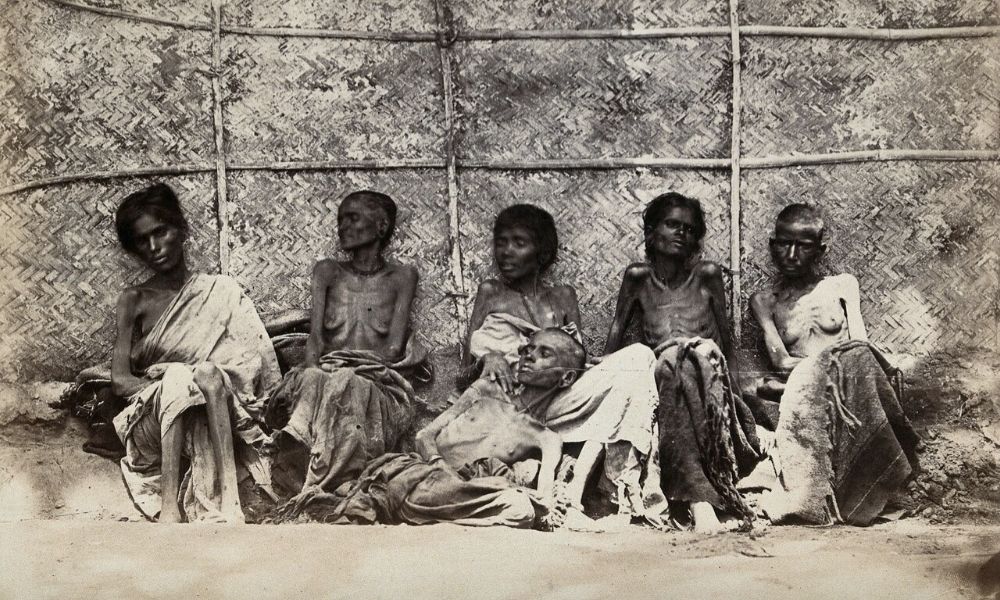
Author: Dr. Jayakumar Srinivasan
Press Release: https://www.esamskriti.com/e/History/Indian-History/Famines-During-British-Rule-1.aspx
More than 50 million died in famines during British rule, yet many school text books do not mention about them, or say thousands died. Read all about the famines.
To read the same article in Tamil please click on PDF.
Our team was asked by a State Government SCERT Textbook Board to review 6 to 8 standard Social Sciences textbook. We made many recommendations for change of content. The State adopted about half of those suggestions. Let us look at one example.
In the context of the Zamindari system, take a look at the following extract from the 8th standard textbook 1

It is true that the British policies ruined our agricultural system. But let us draw our attention to the sentence “There were great famines which killed thousands of people”.
A famine is a situation where there is an extreme scarcity of food, especially grains. Many of us many not have had a first hand-experience of a famine because the last famine was in 1943. However, much research has been done on the study of famines in India, especially during the colonial period.
In an important book Late Victorian Holocausts 2, summarized by Fred Magdoff 3, Mike Davis mentions that there were 17 famines in the 2,000 years before British rule. In comparison, in the 120 years of British rule, there were 31 serious famines. Davis argues that the seeds of underdevelopment in what later became known as the Third World were sown in this era of High Imperialism, as the price for capitalist modernization was paid in the currency of millions of peasants’ lives. This fact should impel us to understand the British role in creating intense famines in India.
Here is a list of some major famines during British rule in India. 4
| Year | Name | Region | Deaths | Comment |
| 1769–70 | Great Bengal Famine | Bihar, Northern and Central Bengal | 10 Million | About one third of the then population of Bengal |
| 1783–84 | Chalisa famine | Delhi,UP, Punjab,Rajasthan, Kashmir | 11 Million | Severe famine. Large areas were depopulated. |
| 1791–92 | Doji bara famineorSkull famine | Hyderabad,Central India,Deccan,Gujarat, Southern Rajasthan | 11 Million | One of the most severe famines known. People died in such numbers that they could not be cremated or buried. |
| 1860–61 | Upper Doab | Rajasthan | 2 Million | |
| 1865-67 | Orissa famine | Bihar, Orissa, Parts of Southern India | 1 Million | The British Secretary of State for India, Lord Salisbury, did nothing for two months, by which time a million people had died |
| 1868–70 | Rajputana famine | Rajasthan | 1.5 Million | |
| 1876–78 | Great Madras Famine | Mysore and Hyderabad States (Madras Presidency) | 6-10 Mil | |
| 1896–97 | Indian famine | Rajasthan, parts of Central India and Hyderabad | 5 Million | |
| 1943–44 | Bengal famine | Bengal | 3.6 Million | 1.5 from starvation; 2.1 from epidemics. |
In an 1883 Volume on Rural Bengal 5, W. Hunter gives a vivid and disturbing picture of the 1770 Bengal Famine, “All through the stifling summer of 1770 the people went on dying. The husbandmen sold their cattle; they sold their implements of agriculture; they devoured their seed-grain; they sold their sons and daughters, till … no buyer of children could be found; they ate the leaves of trees and the grass of the field; and in June, 1770, the Resident at the Durbar affirmed that the living were feeding on the dead.
Day and night a torrent of famished and disease-stricken wretches poured into the great cities. …pestilence had broken out. … we find small-pox at Moorshedabad, … The streets were blocked up with … heaps of the dying and dead. … even the dogs and jackals, the public scavengers of the East, became unable to accomplish their revolting work, and the multitude of mangled and festering corpses at length threatened the existence of the citizens.
Starving and shelter less crowds crawled despairingly from one deserted village to another in a vain search for food, or a resting-place in which to hide themselves from the rain. The epidemics incident to the season were thus spread over the whole country; … Millions of famished wretches died in the struggle to live … their last gaze being probably fixed on the densely-covered fields that would ripen only a little too late for them…”
About a quarter to a third of the population of Bengal starved to death in about a ten-month period. In 1865–66, severe drought struck Odisha and was met by British official inaction.
 Victims pictured in 1877 Reference 4.
Victims pictured in 1877 Reference 4.
 Relief Distribution in Bellary Reference 4. Great Famine 1876 to 78.
Relief Distribution in Bellary Reference 4. Great Famine 1876 to 78.
An important work to understand the role of British during the period 1939-45 (World War II), is Madhusree Mukerjee’s book “Churchill’s Secret War” 6 where she shows that the 20th Century’s greatest hero is also its greatest villain.
When asked to release more grain to India, Churchill said “I hate Indians. They are a beastly people with a beastly religion. The famine was their own fault for breeding like rabbits.” When the Delhi Government sent a telegram to him painting a picture of the horrible devastation and the number of people who had died, his only response was, “Then why hasn’t (Mahatma) Gandhi died yet?”
How to imagine the scale of loss?
The Gaja cyclone of Tamil Nadu in November 2018, which devastated the livelihoods of 500,000 families by leveling coconut, cashew and mango farms killed about 40 people. The 2004 Tsunami killed 230,000 across 14 countries.
The number of Indians who died in famines in Colonial India is 50 million. The scale of loss is incomparable.
What can India do now?
Indian school textbooks should bring out British brutality unambiguously, as these were facts of our history. In the absence of critique of the colonial period, students can come away with the false notion that colonization was the best thing that happened to India.

After our team sent this critique to the State, the Editorial Board replaced one word “thousands” by the word ‘millions” 1. While this is welcome, the text makes it appear that the British rule was benevolent to India. That view needs to be refuted and completely restated that the British were disinterested in the welfare of India!
We can also learn from the West. For example, to memorialize the Jewish Holocaust (where close to 6 Million Jews were deliberately killed in Europe during 1941-45), the US has a museum – called the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum in Washington, D.C. In addition, almost every child going to school in this world likely learns about the Holocaust.
 The infamous Gas Chambers of the Nazi Holocaust Ref 8n Holocaust Museum USA Ref 9.
The infamous Gas Chambers of the Nazi Holocaust Ref 8n Holocaust Museum USA Ref 9.
India should establish monuments in West Bengal and other places to memorialize this genocide that killed as many people as the World War I (40 Million), and World War II (60 Million).
What were factors contributing to an increased incidence and severity of famines during the British rule of India? We will review this in a future article.
References
1. Social Studies, Class VIII, Hyderabad: SCERT, Telangana, 2018.
2. M. Davis, Late Victorian Holocausts: El Niño Famines and the Making of the Third World, Verso Books, 2017.
3. F. Magdoff, “Late Victorian Holocausts: El Niño Famines and the Making of the Third World. By Mike Davis 2001. Verso, London and New York,” Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems, vol. 20, pp. 190-192, 2007.
4. “Timelines of Major Famines in India during British Rule.” (Online).
5. W. W. Hunter, “Annals Of Rural Bengal,” vol. 1, 1883.
6. M. Mukerjee, Churchill’s Secret War: The British Empire and the Ravaging of India during World War II, India Penguin, 2018.
7.”Bengal famine of 1943″. To read Bengal famine and Responsibility for Holocaust
8. G. Will, “A showcase of the vilest and noblest manifestations of humanity,” 26 April 2018.
You may like
articles
भारतीय कास्ट-व्यवस्था में दुनियाभर के लोगों की इतनी दिलचस्पी क्यों ?
Published
4 years agoon
January 14, 2020By
ihar
अन्य देशों के विपरीत भारत में कास्ट-व्यवस्था को सामाजिक विशिष्टता के रूप में प्रस्तुत करने की एक अनोखी प्रवृत्ति रही है। जाहिर है, पश्चिमी दुनिया में व्याप्त सामाजिक उंच-नीच(अनुक्रम) और बहिष्कार के इतिहास पर पर्याप्त ध्यान नहीं दिया जाता है, न ही ब्रिटिश उपनिवेश के अधीन भारत में सामाजिक वर्गीकरण के अनोखे विकास की पूरी तरह से सराहना की जाती है।
रत की कास्ट-व्यवस्था और ‘छुआ-छूत’ बड़ी संख्या में सामाजिक विज्ञान शोधकर्ताओं, इतिहासकारों और यहां तक कि आधुनिक समय में आम जनता के लिए गहरी रुचि का विषय रहा है। भारत में व्याप्त कास्ट की धारणाओं ने गैर-भारतीयों के दिमाग में ऐसी गहरी जड़ें जमा ली हैं कि मुझे अक्सर पश्चिमी लोगों के साथ अनौपचारिक बातचीत के दौरान पूछा जाता है कि क्या मैं अगड़ी कास्ट की हूँ?
यह आश्चर्यजनक नहीं है, क्योंकि आज भी अमेरिका में ‘वर्ल्ड सिविलाइजेसन: ग्लोबल एक्सपीरियंस’ (एपी संस्करण) जैसे हाईस्कूल की पाठ्यपुस्तकों में ऐसे पूर्वाग्रहजनित वाक्यों को शामिल किया गया है: ” शायद, भारतीय कास्ट-व्यवस्था एक प्रकार का ऐसा सामाजिक संगठन है जो आधुनिक पश्चिमी समाज के सर्वाधिक महत्त्वपूर्ण सिद्धांतों, जिनपर समाज टिका है, का उल्लंघन करता है।”
आश्चर्यजनक रूप से, खुद भारतीयों ने ‘निम्न कास्ट और अस्पृश्यों के शोषण’ की इन सभी कहानियों को आत्मसात कर लिया है, और किंचित ही कभी इसकी वैधता पर प्रश्न उठाया है, न ही पश्चिमी दुनिया में व्याप्त ऐसी प्रथाओं के बारे में जानना चाहा है| क्या भारत में छोड़कर विश्व भर में वास्तव में कोई कास्ट-व्यवस्था नहीं थी? यूरोप के समृद्ध नागरिकों के शौचालय से मानव मल को खाली करने वाले लोगों के साथ कैसे व्यवहार किया जाता था? मानव-शवों और पशु-शवों को ठिकाना लगाने वाले लोगों के साथ कैसे व्यवहार किया जाता था? क्या ऐसे लोगों को अमीर लोगों के समकक्ष बैठने या अपनी बेटे-बेटियों की उनसे शादी करने का अधिकार था?
अधिकांश लोगों को यह जानकर आश्चर्य होगा कि 20 वीं शताब्दी तक यूरोपीय कास्ट-व्यवस्था के तहत, निचली कास्ट के लोगों का जीवन बहुत दयनीय था। डीफाइल्ड ट्रेड एंड सोशल आउटकास्ट- ऑनर एंड रिचुअल पॉल्यूसन में लेखक कैथी स्टीवर्ट ने 17 वीं शताब्दी के उन सामाजिक समूहों का वर्णन किया है जो “व्यापार की प्रकृति के कारण हीन” थे जैसे जल्लाद, चमार, कब्र खोदने वाले, चरवाहे, नाई-सर्जन, आटा चक्की वाले, लिनन-बुनकर, बो-गेल्डर, अभिनेता, शौचालय सफाईकर्मी, रात्रि-पहरेदार और न्यायिक कारिन्दा।
एम एस स्टीवर्ट इन व्यवसायों को नीच दृष्टि से देखने को रोमन साम्राज्य की देन मानते हैं। “रोमन साम्राज्य के दौरान ‘नीच’ व्यावसायिकों को ‘उच्च’ कुशल कारीगर समूहों और पुरे समाज के द्वारा जनित सामाजिक, आर्थिक, कानूनी और राजनीतिक भेदभाव के विभिन्न रूपों का सामना करना पड़ा| समय के साथ, ‘नीच’ लोगों को अधिकांश समूहों से बाहर कर दिया गया| सर्वाधिक अपमानित वर्गों जैसे जल्लादों और चर्म-कर्मियों को ‘उनएयरलिक्काइट’ (अपमान की एक अवधारणा) नामक प्रथा का शिकार होना पड़ा जिसमे उन्हें लगभग सभी सामान्य समाजिक समूहों से बहिष्कार का सामना करना पड़ा। जल्लादों और चर्म-कर्मियों को कोई भी कंकड़ फेंककर मार सकता था, उन्हें सार्वजनिक स्नान से बहिष्कार, सम्मानपूर्वक दफन करने से इनकार और महज शराब के हक़ से भी इनकार कर दिया जाता था जो उस समाज में आम लोगों को आसानी से उपलब्ध था। यह अपमान आने वाली कई पीढ़ियों को अपने पिता से मिले धरोहर के रूप में भी झेलना पड़ता था। हीनता में ‘छूत’ का माना जाना इस कुरीति की प्रमुख विशेषताओं में से एक है। हीन लोगों के साथ अनौपचारिक संपर्क में आकर या आचरण के कुछ अनुष्ठान नियमों का उल्लंघन करके सम्मानित नागरिक स्वयं को हीं महसूस करते थे। एक उच्च वर्ग के कारीगर के लिए अशुद्ध होना विनाशकारी होता था।एक समूह के जिन लोगों पर अशुद्ध होने का कलंक लगा होता था उन्हें एक प्रकार की सामाजिक मौत का सामना करना पड़ा। उन्हें अपने समाज से बाहर रखा जाता और उनसे उनके व्यवसाय करने का हक़, जो समूह की सदस्यता द्वारा मिलता था, भी छीन लिया जाता था ताकि वह अपनी आजीविका, सामाजिक और राजनीतिक पहचान दोनों खो दें। यहां तक कि व्यक्तिगत संपर्क के माध्यम से छूत का डर इतना खतरनाक होता था कि पड़ोसी और पास खड़े लोग के सामने व्यक्ति मर भी रहा हो तब भी कोई उसकी मदद नहीं करता था। एक नाटकीय उदाहरण एक जल्लाद की पत्नी का है जो 1680 के दशक में उत्तर जर्मन शहर हुसूम में प्रसव में मरने के लिए छोड़ दी गई, क्योंकि मिडवाइफ ने जल्लाद के घर में घुसने से भी इंकार कर दिया था। ”
सम्पूर्ण इतिहास में, कचरे और मल साफ करने का काम करने वालों को कभी भी सम्मान की नजर से नहीं देखा गया। 20 वीं शताब्दी के उत्तरार्ध तक, यूरोप में मानव माल-मूत्र को पखाने के गड्ढे से हाथ से ही साफ किया जाता था। ‘नीच कर्म’ करने वाले निम्न वर्ग के यूरोपीय लोगों को अंग्रेजी में ‘गोंगफर्मर्स’ (फ्रेंच) या ‘गोंग फार्मर्स’ कहा जाता था। क्या आपको लगता है उनका समुचित सम्मान किया जाता था और उन्हें समाज के उच्च वर्ग के साथ स्वतंत्र रूप से घुलने-मिलने की इजाजत थी?
इंग्लैंड के गोंग फार्मर्स को केवल रात में काम करने की इजाजत थी, इसलिए उन्हें ‘नाइटमेन’ भी कहा जाता था। वे उच्च वर्ग के लोगों के घरों में रात को आते थे, पाखाने के गड्ढे को खाली करते थे और उसे शहर की सीमा के बाहर छोड़ आते थे। उन्हें शहर के बाहर कुछ क्षेत्रों में ही रहने की इजाजत थी और दिन के दौरान वे शहर में प्रवेश नहीं कर सकते थे। इस नियम को तोड़ने पर उन्हें गंभीर दंड मिलता था। कमोड के प्रयोग में आने के बाद भी,लंबे समय तक, मल-मूत्र पखाने के गड्ढों में ही बहता था और इसे ‘नाइटमेन’ द्वारा साफ करने की आवश्यकता पड़ती थी।
दुनियाभर में, जब तक सीवेज और मल के परिवहन और प्रबंधन की आधुनिक व्यवस्था अस्तित्व में नहीं आई, तब तक इन श्रमिकों को समाज से बहिष्कृत ही किया जाता था।आधुनिक शहर जब तक लाखों प्रवासियों, जो विविधता और विषमता को बढ़ाने में भी मदद करते थे, के आ जाने से प्रदूषित नहीं हो गए, समुदाय काफी बंद प्रकार के और दूसरों का बहिष्कार करने वाले होते थे।
दिलचस्प बात यह है कि अंग्रेजी शब्द ‘कास्ट’ पोर्तगीज शब्द ‘कस्टा’ से लिया गया है। इसका इस्तेमाल उन स्पेनिश अभिजात वर्गों द्वारा किया जाता था जिन्होंने विजय प्राप्त क्षेत्रों पर शासन किया था। ‘सिस्टेमा डी कास्ट’ या ‘सोसाइडा डी कास्टों’ जैसे शब्दों का इस्तेमाल, 17 वीं और 18 वीं सदी में,स्पेनिश-नियंत्रित अमेरिका और फिलीपींस में मिश्रित प्रजाति वाले लोगों के वर्णन करने के लिए उपयोग होता था। ‘कास्टा’ व्यवस्था ने जन्म, रंग और प्रजाति के आधार पर लोगों को वर्गीकृत किया। एक व्यक्ति जितना अधिक गोरा होता था, उसको उतना अधिक विशेषाधिकार प्राप्त था और कर का बोझ भी कम होता था। कास्टा, ईसाई स्पेन में विकसित रक्त की शुद्धता के विचार का विस्तार था जो बिना यहूदी या मुस्लिम विरासत से कलंकित लोगों के बारे में सूचित करता था। स्पैनिश आक्रमण के वक्त जब पुराने धर्म वापस अपनाने के संदेह पर हजारों परिवर्तित यहूदी और मुस्लिम (यूरोपीय, निम्न वर्ग) को मार दिया गया था तब तक तो ऐसी अवधारणाओं ने काफी गहरी जड़ें जमा ली थी।
एडवर्ड अलसवर्थ रॉस ( प्रिंसिपल्स ऑफ सोशियोलॉजी, 1920) यूरोप की कठोर और सख्त ‘कास्टा’ व्यवस्था का एक विस्तृत विवरण देते हैं और कहते हैं कि यह यूरोपीय समाज के भीतर शक्तियों की देन था। वह कहते है:
“रोमन साम्राज्य पुरुषों को अपने पिता के व्यवसाय का ही पालन करने और अन्य व्यवसाय या जीवन-यापन के तरीकों के बीच एक मुक्त परिसंचरण को रोकने को मजबूर कर रही थी। वह व्यक्ति जिसने अफ्रीका के अनाज को ओस्टिया के सार्वजनिक भंडार तक पहुचाया, मजदूर- जिन्होंने इसे वितरण के लिए ब्रेड बनाया, कसाई – जिसने सामनियम, लुकेनिया, ब्रूटीअम से सुअर लाया, शराब विक्रेता, तेल विक्रेता, सार्वजनिक स्नानघर की भट्टियों में कोयला डालने वाला, पीढ़ी दर पीढ़ी उसी काम को करने को बाध्य थे… इससे बचने का हर दरवाजा बंद कर दिया गया था … लोगों को अपने समूह से इतर शादी करने की इजाजत नहीं थी …किसी प्रकार शाही फरमान हासिल करने के बाद भी नहीं, यहां तक कि शक्तिशाली चर्च भी इस दासता के बंधन को नहीं तोड़ सकते थे।”
भारतीय ‘कास्ट व्यवस्था’ ब्रिटिश उपनिवेशवादियों द्वारा लगाया गया एक पहचान था, पर इस पहचान ने समाजिक विभाजन का सही ढंग से प्रतिनिधित्व नहीं किया। वेदों में, रक्त की शुद्धता , जो यूरोप की कास्ट-व्यवस्था की विशेषता थी, की कोई अवधारणा नहीं थी। दूसरी तरफ, कार्यों और व्यक्तिगत गुणों के आधार पर व्यक्ति का वर्ण निर्धारित करने की अवधारणा थी। भारतीय शब्द “जाति”, जो कि समाज के व्यावसायिक विभाजन को नाई, चमार, मवेशी-पालक, लोहार, धातु श्रमिकों और अन्य व्यापारों के रूप में इंगित करता था, सिर्फ भारत में ही एक अवधारणा नहीं थी (भले ही ‘कारीगरों के समूह’ की अवधारणा का जन्म भारत में ही हुआ था)। दुनिया में बसने वाले हर समाज में, बेटों ने परंपरागत रूप से अपने पिता के व्यवसाय को ही अपनाया। बढई के पुत्र बढई बने। बुनकरों के पुत्र बुनकर बने। ऐसा होना स्वाभाविक भी लगता है क्योंकि बच्चे अपने पिता के व्यापार से अच्छी तरह से परिचित होते थे, और अपने व्यापार की अनोखी विशेषताओं को सम्हालकर गुप्त रख सकते थे।
भारत में, जातियों को विभाजित करने वाली रेखाएं शुरू में धुंधली थीं और लोगों के कुल से हटकर व्यवसाय अपनाने के कई उदहारण भी मिलते हैं| निचली जातियों के संत रवीदास, चोखमेला और कनकदास ने लोगों का सम्मान अर्जित किया और उन्हें ब्राह्मण संतों से कम नहीं माना जाता था। मराठा पेशवा ब्राह्मण थे जो बाद में क्षत्रिय बन गए थे। मराठा राजा शिवाजी जिन्होंने कई साम्राज्यों पर अपनी जीत के बाद उदार ब्राह्मणों के समर्थन से खुद को क्षत्रिय घोषित कर दिया था, को शुरुआत में निचली जाति का माना जाता था| प्रसिद्ध समाजशास्त्री एमएन श्रीनिवास कहते हैं:
“यहां ध्यान देने वाली बात यह है कि एक क्षेत्र में असंख्य छोटी जातियों का समाज में स्पष्ट और स्थायी अधिक्रम नहीं रहता। अधिक्रम का परिवर्तनशील होना ही वास्तविक समाज को काल्पनिक समाज से अलग करता है। वर्ण-व्यवस्था जाति व्यवस्था की वास्तविकताओं की गलत व्याख्या का कारण रहा है। हाल के क्षेत्र-शोध से यह बात सामने आई है कि अधिक्रम में जाति की स्थिति एक गांव से दूसरे गांव में भिन्न हो सकती है। अलग-अलग जगहों में सामजिक अधिक्रम परिवर्तनशील होता है और जातियां समय के साथ बदलती रहती हैं| इतना ही नहीं, सामाजिक ओहदा कुछ हद तक महज स्थानीय भी होता है।”
यह भी ध्यान दिया जाना चाहिए कि यूरोप के विपरीत, भारत में उच्च और निम्न वर्ग का विभाजन कभी भी आर्थिक विषमता के कारण नहीं हुई। ब्राह्मण परंपरागत रूप से सबसे गरीब, प्रायः याचक ही होते थे। वैश्य और शूद्र व्यापारी प्रायः अमीर होते थे और अक्सर ब्राह्मणों की सेवा लेते थे। आमतौर पर, भूमि क्षत्रिय, वैश्य और शुद्रों के स्वामित्व में थी। प्रसिद्ध गणितज्ञ आर्यभट्ट स्वयं एक गैर-ब्राह्मण थे और फिर भी उनके अधीन नंबूदरी ब्राह्मण शिक्षा ग्रहण करते थे। आज भी, सैकड़ों ब्राह्मण जाति के लोग भारत में शौचालयों की सफाई में कार्यरत हैं, जबकि किसी को भी अमेरिका में एक स्वेत व्यक्ति द्वारा एक कचरा ट्रक चलाना हैरानी की बात लगेगी।
इतिहासकार धर्मपाल ने 18 वीं शताब्दी में स्वदेसी शिक्षा प्रणाली पर अपनी किताब ‘द ब्यूटीफुल ट्री’ में लिखा है कि मद्रास, पंजाब और बंगाल प्रेसीडेंसी में किये गए ब्रिटिश सर्वेक्षणों ने भारत में बच्चों के विद्यालयों में व्यापक नामांकन का खुलासा किया। लगभग हर गांव में एक विद्यालय था। कई विद्यालयों में शूद्र बच्चे ब्राह्मण बच्चों से अधिक संख्या में थे। इन स्कूलों को धीरे-धीरे बंद कर दिया गया क्योंकि ब्रिटिश शासन में गरीबी व्यापक हो गई थी और ग्रामीण नौकरियों की तलाश में शहरों को चले गए।
स्पेनिश औपनिवेशिक कला – मेक्सिको की कास्टा प्रणाली।
विदेशी आक्रमणों और “फूट डालो शासन करो ” की ब्रिटिश नीति जैसे विभिन्न कारकों के कारण जाति विभाजन अधिक कठोर हो गया। जब तक अंग्रेजों ने 1881 से विभिन्न उपनामों को विभिन्न जातियों में सूचीबद्ध करने के लिए व्यापक जनगणना नहीं किया, तब तक अधिकांश भारतीय जातियों के अधिक्रम से अवगत नहीं थे। आम तौर पर, कुछ परिवार के नाम एक गांव में एक विशेष जाति से जुड़े थे और दूसरे गांव में एक अलग जाति के साथ। अचानक, जनगणना के कारण जातीय विभाजन की रेखा प्रगाढ़ हो गयी। अंग्रेजों द्वारा जातीय पहचान पर इसलिए इतना जोर दिया ताकि भारतीय समाज जातियों में बटे रहें और अंग्रेजों के खिलाफ एकजुट न हो सकें| इसके कारण जातियों में आपस में गहरे विवाद पैदा हो गए| ब्रिटिशों द्वारा कई अनुसूचित जातियों और जनजातियों को आपराधिक श्रेणियों में रखने से भी जातीय रेखाएं प्रगाढ़ हो गयीं जो स्वतंत्र भारत के लिए विनाशकारी परिणाम लेकर आई। विडम्बना यह है कि वर्ग और कास्ट में विश्वास रखने वाले ब्रिटिश ने भारतीय जातियों को सूचीबद्ध किया, उन्होंने अंग्रेजी महिलाओं को भारतीय पुरुषों से शादी करने की इजाजत नहीं दी, जबकि भारतीय महिलाओं को अंग्रेजों द्वारा रखैल की तरह अपनाने में भी उन्हें कोई आपत्ति नहीं थी।
यह याद रखना चाहिए कि भारत की व्यवसाय आधारित जाति प्रणाली की ढीली संरचना को बदनाम और सख्त करना ईसाई मिशनरियों की रणनीति का हिस्सा था। गवर्नर जनरल जॉन शोर के ईसाई धर्म के क्लैफम संप्रदाय के सदस्य बनने के बाद भारत में मिशनरी गतिविधि में काफी वृद्धि हुई। अपने “अंधविश्वास वाले धर्म” के कारण हिंदुओं को “मानव जाति का सबसे पिछड़ा और असभ्य लोग” घोषित किया गया था। विलियम विल्बरफोर्स, जो दास-विरोध के प्रणेता माने जाते थे और क्लैफम सेक्ट के सदस्य भी थे, ने 1813 ई. में हाउस ऑफ कॉमन्स में घोषित किया कि हिंदुओं को अपने धर्म से मुक्त करना हर ईसाई का पवित्र कर्तव्य है, वैसे ही जैसे अफ्रीका को गुलामी से मुक्त कराना।
दुनिया में कोई भी देश असमानताओं से मुक्त नहीं है। ऐसा होना अधिक पैसे और अधिक शक्ति के लिए निरंतर मानव प्रयास के द्वारा भी सुनिश्चित होता है। भेदभाव व्यापक रूप से फैला हुआ है और गैर-ईसाई, गैर-मुस्लिम, काले, समलैंगिक, महिलाएं, एड्स रोगी या कुष्ठरोगी इसके प्रमुख शिकार रहे हैं। पश्चिमी समाजों में ऐतिहासिक रूप से प्रचलित नस्लवाद जो आज भी विभिन्न रूपों में जारी है, यह भी घातक कास्ट व्यवस्था का एक रूप ही है। होलोकॉस्ट के लिए नाज़ीवाद और यहूदी-विरोध को दोषी ठहराया जाता है, लेकिन शायद ही लोगों ने इसे कास्ट-व्यवस्था के बुरे परिणाम के रूप में देखा है| यहां तक कि संयुक्त राष्ट्र सुरक्षा परिषद में केवल पांच स्थायी सदस्यों का होना भी कास्ट-व्यवस्था है, जिनके पास वीटो शक्तियां हैं। आइवी लीग विश्वविद्यालयों के स्नातक और विशिष्ट क्लब के सदस्य भी अपने स्वयं के कास्ट विशेषाधिकारों का फायदा उठाते हैं।
यह तर्क दिया जा सकता है कि भारत ने ऐतिहासिक रूप से वंचित जातियों की सहायता के लिए “आरक्षण” नामक दुनिया की सबसे बड़ी सकारात्मक योजना को लागू किया है। सरकारी स्कूलों और कॉलेजों में आरक्षित स्लॉट के साथ, सरकारी सेवाओं में पदों और चुनावी निर्वाचन क्षेत्रों में आरक्षित सीटों के साथ समावेशी होने का एक बड़ा प्रयास किया गया है। भले ही इन प्रयासों के अच्छे परिणाम मिले हों या नतीजतन “विरोधी कास्ट व्यवस्था” ने जन्म ले लिया हो, यह जांच का विषय है।
भारत में कास्ट-पहचान का आधुनिक वर्गीकरण और इसकी विचित्र अभिव्यक्ति ब्रिटिश और भारतीय सरकारों की संस्थागत नीतियों का बुरा परिणाम है जिसमे मार्क्सवादियों और अल्पसंख्यकों, साथ ही साथ गरीबी और विकास के अवसरों की कमी का बड़ा योगदान है। कास्ट-पहचान हिंदू परंपराओं में समाज के मूल वर्गीकरण की किसी कल्पना की विकृति की देन नहीं है।
यह सबसे उपयुक्त समय है कि दुनिया और स्वयं भारतीयों को भारत को कास्ट-व्यवस्था के चश्मे से देखना बंद कर देना चाहिए और दुनिया की हर हिस्से में कास्ट-व्यवस्था की शुरुआत के साथ-साथ सामाजिक-आर्थिक ओहदों को समझने का प्रयास करना चाहिए। इतने लंबे समय तक पश्चिमी शोधकर्ताओं के सामाजिक और मानव विज्ञान अध्ययनों का विषय रहने के कारण भारतीयों ने भी यह मानना शुरू कर दिया है कि प्रयोगशाला में नमूने की तरह, उनकी जगह भी माइक्रोस्कोप के नीचे है। यह लेंस को उलटे करने का समय है। भारत के बाहर एक पूरी दुनिया भारतीय परिप्रेक्ष्य से जांचे जाने और समझे जाने की प्रतीक्षा कर रही है।
The article has been translated from English into Hindi by Satyam
Disclaimer: The facts and opinions expressed within this article are the personal opinions of the author. IndiaFacts does not assume any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, completeness,suitability,or validity of any information in this article.

Author: Dr. Jayakumar Srinivasan
Press Release: https://www.esamskriti.com/e/Spirituality/Education/The-Story-Of-Pythagoras-1.aspx
The Pythagoras theorem is studied by almost every high school or college student all over the world. We have used this theorem of squares of the lengths of sides of the right angled triangle in solving numerous problems in geometry for years.
Pythagoras lived from 570 to 495 BCE, i.e. for about 75 years. Several scholars such as Albert Burk (1) and others say that Pythagoras visited and lived in India where he learned Indian Philosophy and Sciences. Dr. Raj Vedam, in his talks (2) narrates the story of Pyathagoras’ visit to India. Burk suggests that he learned in Sourthern India. Raj Vedam postulates that Pythagoras could have studied at Kanchipuram. Even though we are told that Kanchipuram was the capital of the Pallava Kingdom, its history is significantly older.
When Pythagoras returned to Greece, he was called a madman because he had become vegetarian! His diet was predominantly based on nuts, corn and fruit. He set up an education system based on the Gurukulam style of India.
To read article in English in PDF
To read article in Tamil in PDF
To read all articles by Author
Also read
1 Talks on Maths in metrical form

Author: Dr. Jayakumar Srinivasan
Press Release: https://www.esamskriti.com/e/History/Indian-History/Was-India-Always-A-Poor-Country-1.aspx
To read article in Tamil in PDF.
Today, many people consider India to be a developing country, or a polite way of saying that Indians are “poor”. There is truth in this observation. Despite the dazzle and comforts of city life, air travel, multi-storied malls and Smart Phones, the majority of Indians lead a rough life. People attribute India’s continued poverty to many causes such as government corruption and ineptitude, poor infrastructure, social inequality, communal conflicts, and lack of innovative spirit.
In the same breath, we also say that India is one of the oldest civilizations, i.e. that it has one of the longest histories of any country, or rather people lived here for many thousands of years continuously. On top of that, we are told that the British made Indians civilized and prosperous.
In this article, the question we are asking is “Was the geography that we now call India alwayseconomically backward?” Specifically, we are focusing on the economy aspect of overall prosperity.
How does one measure economic prosperity? For example, today, we say that the USA is a very prosperous country. What does this mean?
We use a number called GDP (“Gross Domestic Product”) that is calculated for every country. Higher the GDP number, more prosperous a country is. GDP is supposed to measure economic activity of a country. GDP is defined as the value of all goods and services produced by a country in one year. The more a country produces, which then gets consumed locally or exported globally, the higher the GDP. For example, today, the world buys expensive items like Hewlett Packard laptops, Apple iPhones, and Boeing aircraft from the USA. People in the USA also consume large quantities of goods and services, much more than anywhere else in the world. Hence, it is no surprise that the GDP of USA is the highest in the world today.
To illustrate how we are going to use GDP, I performed a simple analysis of GDP data for the year 2017 published by the International Monetary Fund (1):
| 2017 GDP comparison in Trillion US Dollars | |
| GDP of USA | $19.4 |
| GDP of Entire World | $ 80 |
| America’s Share of World Economy | 19.4/80 = ~25% |
| GDP of India | $ 2.6 |
| India’s Share of World Economy | 2.6/80 = 3.2% |
This means that when the world citizen spends Rs. 100, Rs. 25 of that revenue goes to the USA. Now you can imagine why USA is economically prosperous, even without visiting it!
Now we should be able to understand statements such as this in the news “PM Narendra Modi today called for targeting double-digit GDP growth … and said India’s share in world trade has to more than double to 3.4 per cent.” (2)
Now, how are we to understand the economy of countries in the past? Indians must thank an economist Angus Maddison (3). He was a Professor of Economics in The Netherlands. He extensively research to compare the economies of many countries and how they evolved over time. He went backward in time – not a year, not a decade, not a century, but two thousand years!
Prof. Maddison collected a lot of data over many years. The best way to understand what he found is by looking at the chart below (4).
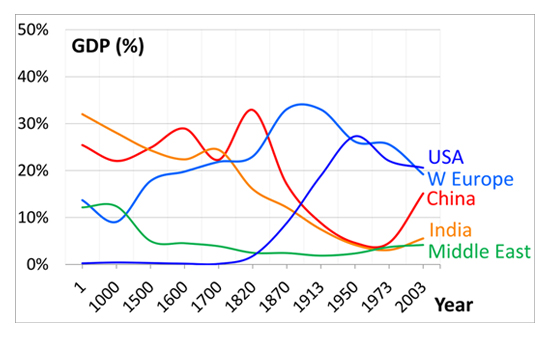
Looking at this chart, we can make the following observations:
1. India was the most prosperous country for the first 1,500 years of the Current Era
2. India’s share of the global GDP started plummeting from a high of 25% since late 1700 all the way to under 5% at Independence.
3. After the British entered India and established their regime, the economy of Western Europe increases dramatically from around 1800.
4. After Europeans establish settlements in America and began slavery, a non-existent American economy skyrockets starting in 1800s.
5. The trend for India has been reversing since the 1970’s.
So, if I were to ask the question “How economically prosperous was India 300 years ago”, we should be able to see that “India was as relatively prosperous then as USA is today!”
S. Gurumurthy’s talk at IIT Bombay in 2010 (5) provides a very good introduction to this topic.
Pay closer attention to the economic trends of India and Western Europe. Less than a century after the British entered India and establish themselves firmly, European economy begins skyrocketing for almost 150 years. Raj Vedam (6) says that this is not a coincidence. He attributes this to transference of wealth from India.
Let us see what the plundering British themselves had to say. Robert Clive (1725-74) was the Commander-in-Chief of British India. He created ownership of the lands of what is today India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, and established a process of funneling wealth out of India to Britain. He said that India was “a country of inexhaustible riches and one which cannot fail to make its masters the richest corporation in the world” (7). At that time, the state of “Bengal” alone, which was the richest “state” in India, was richer than the entire Britain!
When an American philosopher Will Durant visited India in 1930, 175 years after Robert Clive’s planned campaign to destroy India began, Durant was so horrified at the destruction wrought by the British (8) that, instead of pursuing his goal of writing his book “The Story of Civilization”, he took up writing to inspire Indians to fight for Independence. In what he terms as “The Rape of a Continent”, he says “But I saw such things in India as made me feel that study and writing were frivolous things in the presence of a people-one-fifth of the human race – suffering poverty and oppression bitterer than any to be found elsewhere on the earth…” Raj Vedam highlights actions by the British that choked India (6).
●The cost of British conquests (including first and second world wars), developments in Britain, and administration of India, were all charged to Indians.
●Indians were forced to sell cheap and buy exorbitantly.
●Indians were taxed twice as high as in England and thrice as in Scotland.
●Millions of dollars’ worth of bribes from rulers who were dependent on favours and guns.
Hence, it is accurate to say that the British rule decimated Indian economy and ruined India. Yet, today, our children are taught that it is “the caste oppression” that made India poor!
In conclusion, India was one of the most economically prosperous countries in the world for a good bit of the known past. The British rule is probably the most significant factor that contributed to India’s poverty.
Let us remind ourselves that “Colonization” is never beneficial for the colonized people. If we study history properly, we will likely find that every colonized country was culturally and economically prosperous, and each such country is in various states of struggle or ruin today.
References
1. “World Economic Outlook Database“, International Monetary Fund, 17 April 2018.
2. “PM Narendra Modi seeks double-digit GDP growth, raising India’s share in world trade”, The Economic Times, June 22, 2018.
3. Maddison A, “Contours of the World Economy 1-2030 AD”, Oxford University Press, 2007.
4. Hunter, Tracy M., Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0,
5. S. Gurumurthy, speech at IIT Bombay Hindustan Times Avenue 2010 (Full),
6. Raj Vedam, “Indian civilization: The Untold Story”, Talk at Srijan Foundation, New Delhi, February 2018.
7. J. Albert Rorabacher, “Property, Land, Revenue, and Policy: The East India Company, C.1757–1825”, Routledge, 2017.
8. Will Durant, “The Case for India”, Simon and Schuster, New York, 1930.Also read

Bharat Varsh – A Cradle of Civilzation – Panel Discussion

Ram Katha in Bengal’s Heritage and Culture

“Ramayana Across Asia and Beyond” – An IHAR sponsored event was held on Capitol Hill on Jan 10, 2024

Launch of IHAR in Odisha

Matching Oral History With Indic Chronology ( A Discourse by Swami Vidyadhishananda)

Bringing our Gods back home – A Conversation with Shri Vijay Kumar

Panel Discussion on Sati

Bharat Varsh – A Cradle of Civilzation – Panel Discussion

The Untold History Of Ancient India – A Scientific Narration

Some new evidence in Veda Shakhas about their Epoch by Shri Mrugendra Vinod ji

The Untold History Of Ancient India – A Scientific Narration

Some new evidence in Veda Shakhas about their Epoch by Shri Mrugendra Vinod ji

West Bengal’s textbooks must reflect true heritage – Sahana Singh at webinar ‘Vision Bengal’

Bringing our Gods back home – A Conversation with Shri Vijay Kumar

India’s Leadership in shaping the Post Covid world order by Dr Sreeram Sunder Chaulia
Trending
-

 Videos11 months ago
Videos11 months agoBringing our Gods back home – A Conversation with Shri Vijay Kumar
-

 Videos9 years ago
Videos9 years agoPanel Discussion on Sati
-

 Events2 months ago
Events2 months agoBharat Varsh – A Cradle of Civilzation – Panel Discussion
-

 Videos10 months ago
Videos10 months agoThe Untold History Of Ancient India – A Scientific Narration
-

 Videos11 months ago
Videos11 months agoSome new evidence in Veda Shakhas about their Epoch by Shri Mrugendra Vinod ji
